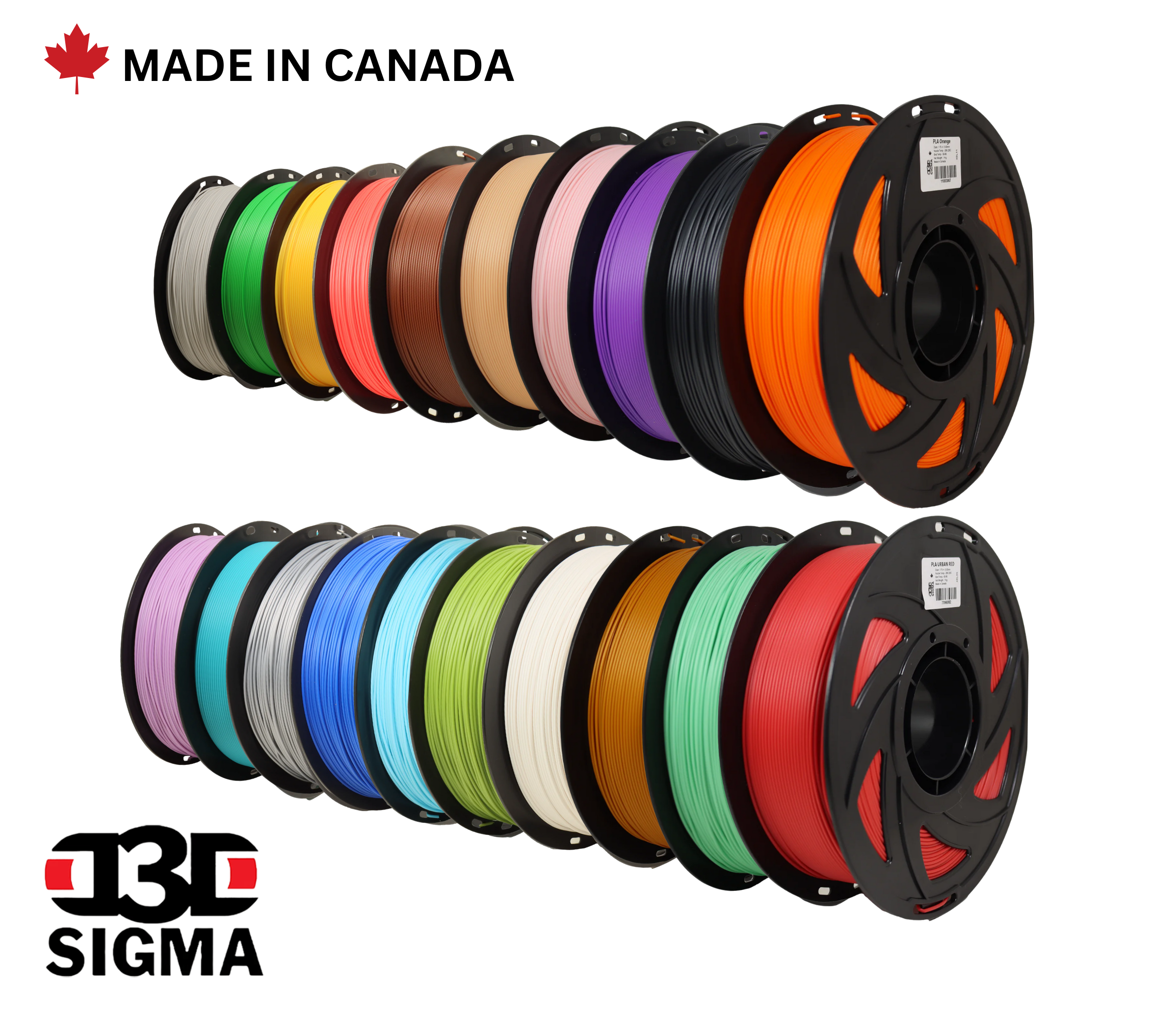
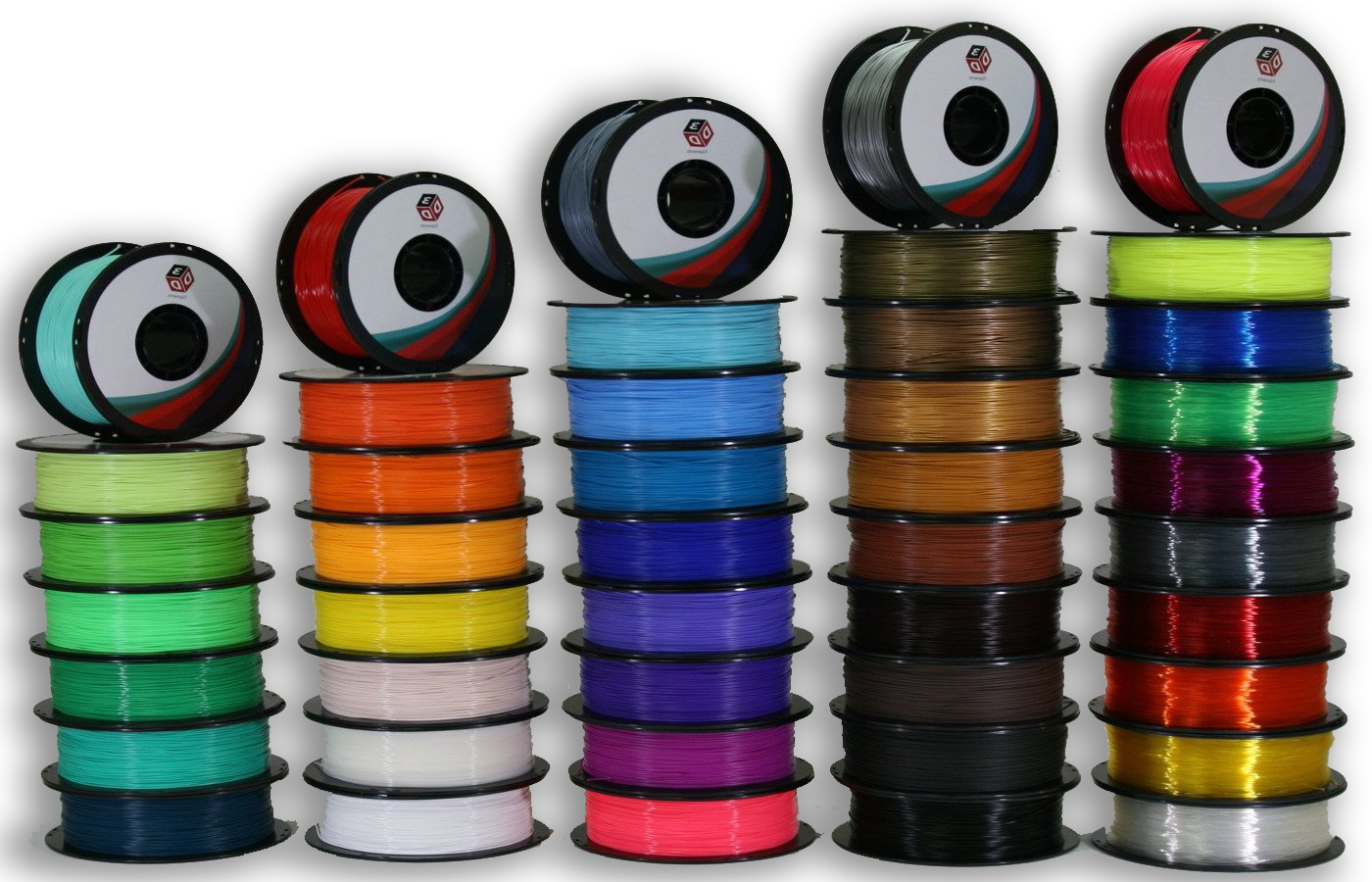
Menu
You have no recently viewed items.
Categories
Categories
Categories
-
Categories -
Offer Of The Week
- Financing
- 3D Printing
- Support
- Blog
-
Browsing History
You have no recently viewed items.